- Newtonian Systems show constant viscosity, independent of applied shear rate.
- Newtonian Systems is a fluid whose flow behavior follows Newton’s law of viscosity, which means:
- The viscosity remains constant regardless of the shear rate or the force applied.
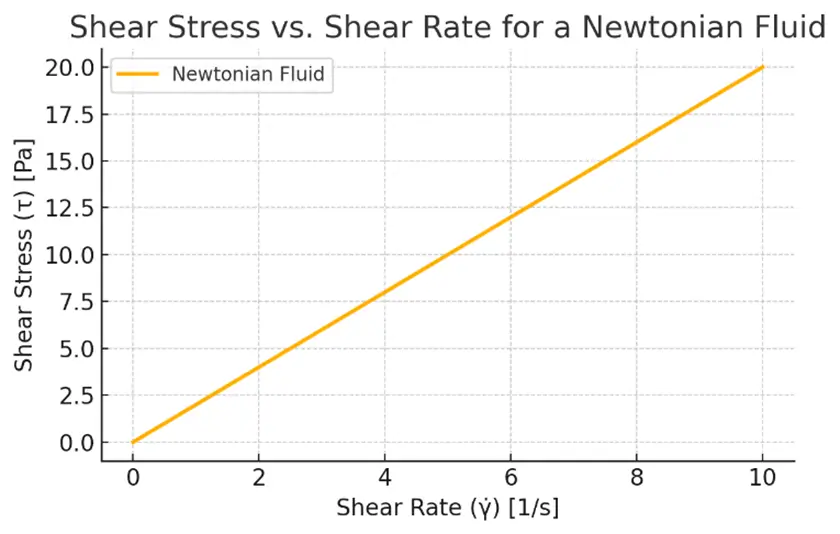
- The relationship between shear stress (F/A) and shear rate (du/dx) is linear.
Definition:
- A Newtonian fluid is one for which the shear stress is directly proportional to the shear rate.
Advertisements
Mathematical Form (Newton’s Law of Flow):
$\tau = \eta \cdot \gamma$
Where:
- τ = shear stress (force per unit area, N/m² or dynes/cm²)
- η = viscosity (resistance to flow)
- γ = shear rate (rate of change of velocity across the fluid)
Advertisements
Graphical Representation:
If you plot:
Advertisements
- X-axis: Shear rate γ
- Y-axis: Shear stress τ
Examples in Pharmaceutics:
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

