Phenacaine is an ester-type local anesthetic used mainly in ophthalmology for surface eye anesthesia.
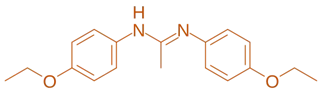
Structure of Phenacaine
- It is an amino benzoic acid derivative with a propyl ester group, providing effective local anesthetic properties.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₂₀N₂O₂
Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse conduction.
- Membrane Stabilization: Enhances nerve membrane stability, reducing excitability.
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Applied in dental procedures, minor surgeries, and ophthalmic preparations.
- Topical Preparations: Used in creams, gels, and sprays for localized pain relief.
- Ophthalmic Anesthesia: Employed in eye surgeries for corneal numbing.
Side Effects of Phenacaine
- Local Irritation: Redness, swelling, or discomfort at the application site.
- Systemic Toxicity: Rare but possible with excessive use, leading to CNS and cardiovascular effects.

