- Physical Properties in Pre-formulation Studies impact drug solubility, stability, and formulation efficiency.
- Understanding Physical Properties in Pre-formulation Studies like crystalline vs. amorphous state helps optimize drug performance and bioavailability.
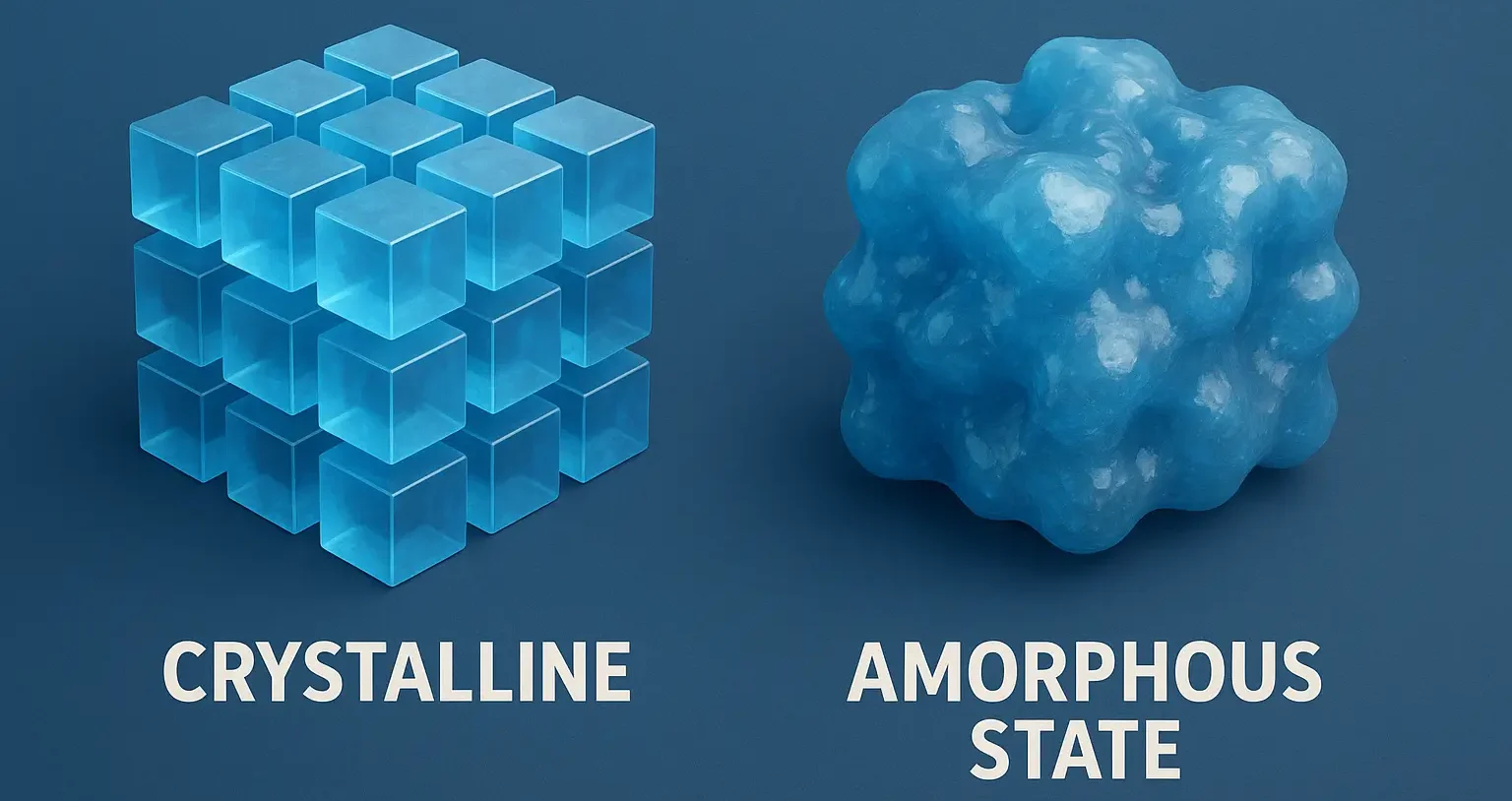
Physical Form: Crystalline vs. Amorphous State
Physical form: Crystalline vs. Amorphous state indicates whether a drug has an ordered (crystalline) or disordered (amorphous) molecular structure, influencing formulation.
1. Crystalline Form:
-
Definition:
- A crystalline drug has a well-defined and ordered molecular structure. Molecules are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern known as a lattice structure.
-
Characteristics:
- High melting point due to strong intermolecular forces.
- Higher stability compared to amorphous forms.
- Typically, less soluble in water, leading to slower dissolution rates and possibly reduced bioavailability.
-
Importance:
- Suitable for long-term stability.
- Used when slower drug release is desired.
2. Amorphous Form:
-
Definition:
- An amorphous drug lacks a defined molecular arrangement, resulting in a random or disordered structure.
-
Characteristics:
- Lower melting point and reduced stability.
- Higher solubility and faster dissolution rates due to higher free energy.
-
Importance:
- Ideal for enhancing bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
- Requires stabilization techniques (e.g., polymers or solid dispersions) to prevent recrystallization during storage.
Comparison Table:
| Property | Crystalline Form | Amorphous Form |
| Structure | Ordered molecular lattice | Disordered structure |
| Melting Point | Defined | No defined melting point |
| Diffraction | Sharp patterns (X-ray visible) | Broad, less defined patterns |
| Stability | More stable | Less stable, prone to recrystallization |
| Solubility | Lower solubility | Higher solubility and faster dissolution |
| Bioavailability | Lower due to low solubility | Higher due to increased solubility |
| Advantages | Predictable, easier to handle | Improved drug delivery, higher solubility |
| Disadvantages | Lower solubility, polymorphism variability | Less stable, sensitive to environment |
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!