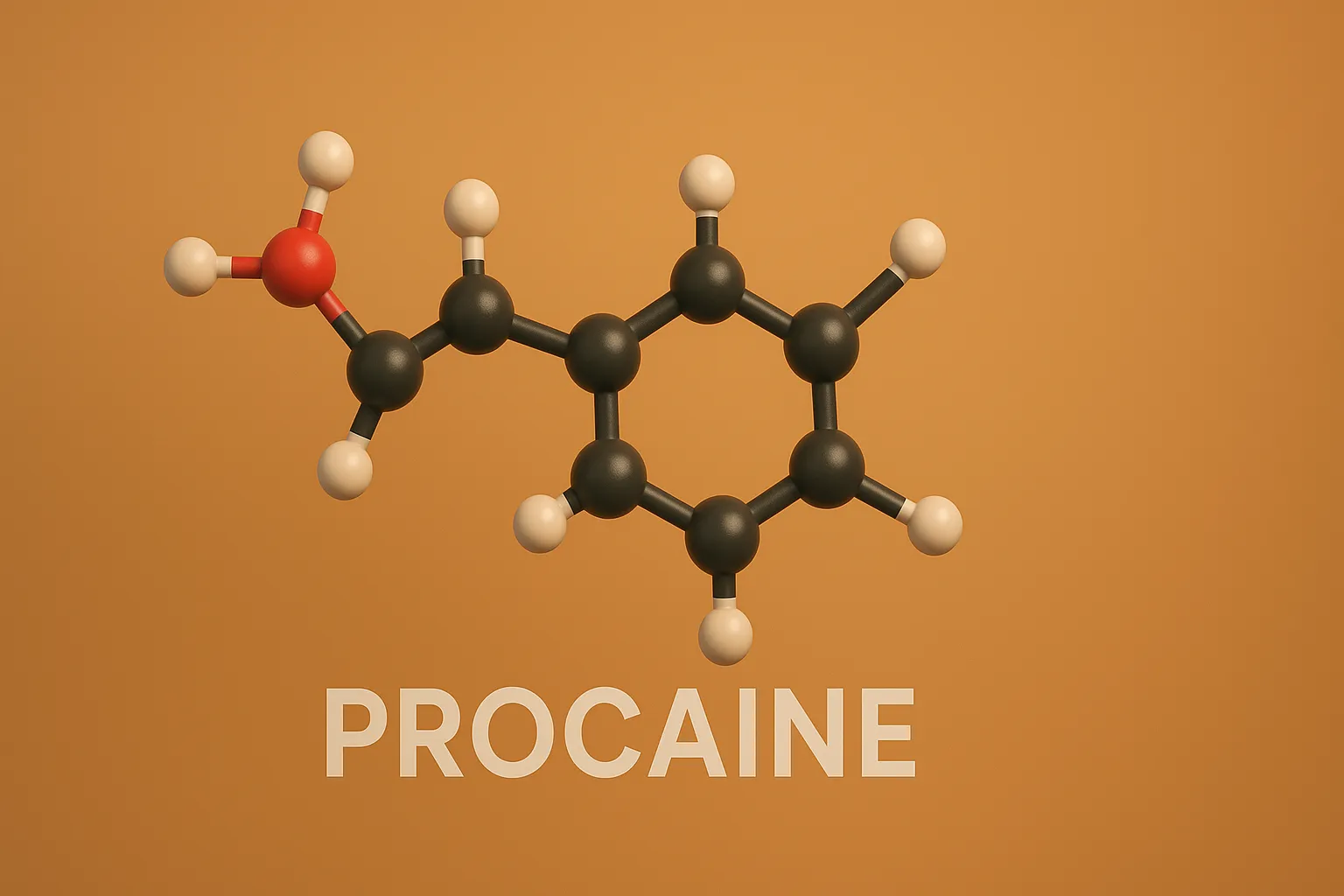
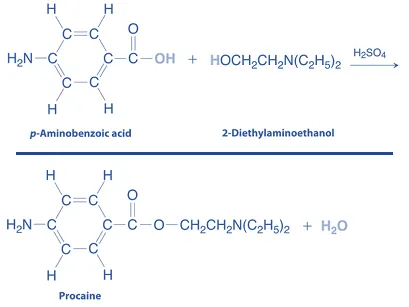
Procaine is an ester-type local anesthetic used for infiltration and nerve block anesthesia by blocking nerve impulse conduction.
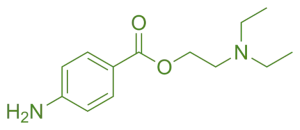
Structure of Procaine
- Procaine is a classic amino benzoic acid derivative with an ethyl ester group, enhancing its solubility and anesthetic duration.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₂₁N₃O₂
Mode of Action
- Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Inhibition: Blocks sodium influx, preventing nerve impulse conduction.
- Membrane Stabilization: Decreases nerve excitability by altering membrane permeability.
Uses
- Local Anesthesia: Used in dental procedures, minor surgeries, and cosmetic applications.
- Topical Preparations: Applied to mucous membranes and skin for temporary numbing.
- Infiltration Anesthesia: Injected around tissues to block nerve signals in a specific area.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Ester Group: Facilitates rapid onset and short duration of action due to quick hydrolysis.
- Diethylamino Group: Enhances lipophilicity, improving membrane penetration and anesthetic efficacy.
- Benzene Ring Substitution: Modifications can influence potency and duration of anesthesia.
Synthesis of Procaine