Source and Occurrence of Quinine
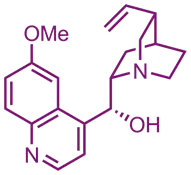
- Quinine is obtained from the bark of the cinchona tree (Cinchona officinalis, Cinchona bark).
- It is a bitter alkaloid with antimalarial properties.
Advertisements

Isolation
-
Extraction:
- Bark Processing: The bark is dried and powdered.
- Alkaloid Extraction: Mixed with an acidic aqueous solution (e.g., dilute HCl) to convert quinine into its water-soluble salt.
-
Purification:
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction: Basify the solution with NaOH to free the quinine base, which is then extracted into an organic solvent like ether or chloroform.
- Crystallization: Quinine is crystallized from the organic phase by adding a non-solvent (e.g., ethanol).
-
Chromatography:
- Column Chromatography: Further purification using silica gel columns and appropriate solvent systems.
Advertisements
Identification
-
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: White crystalline solid.
- Melting Point: Approximately 176-180°C.
- Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, ether, and slightly soluble in water.
-
Spectroscopic Techniques:
- IR Spectroscopy: Identifies functional groups such as quinoline ring and hydroxyl groups.
- NMR Spectroscopy:
- ¹H NMR: Characteristic signals from the quinoline moiety and ethyl side chain.
- ¹³C NMR: Confirms the quinoline ring structure.
- Mass Spectrometry: Molecular ion peak at m/z 324 (free base).
-
Chromatographic Techniques:
- HPLC: For purity assessment and quantification.
- TLC: Used during extraction and purification stages.
Analysis
-
Quantitative Analysis:
- HPLC with UV Detection: Standard method for quinine quantification, especially in pharmaceutical formulations.
- Spectrophotometric Methods: Utilizing specific detection wavelengths.
-
Quality Control:
- Ensuring the absence of other cinchona alkaloids like quinidine.
- Confirming structural integrity through spectroscopic data.
Advertisements
Applications and Significance of Quinine
- Quinine is historically significant as the first effective treatment for malaria.
- It is also used in tonic water and serves as a precursor for synthesizing other antimalarial drugs.
- Its bitter taste has led to widespread use in beverages and flavorings.

