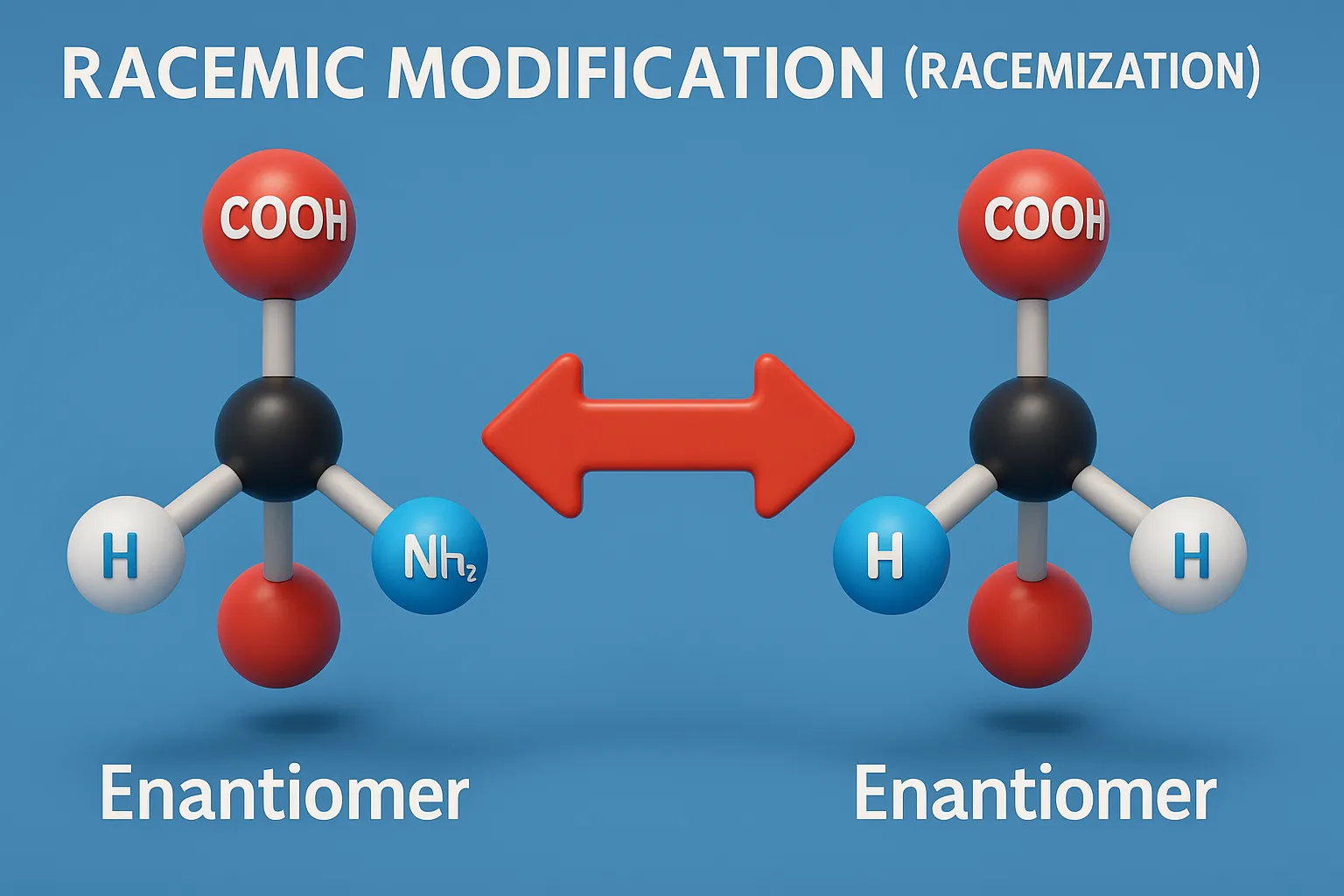
- Racemic Modification (Racemization) is the formation of an equimolar mixture of two enantiomers, making the mixture optically inactive.
What is a Racemic Mixture?
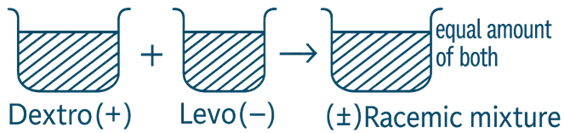
- A racemic mixture (also called a racemate) is a 1:1 mixture of two enantiomers of a chiral compound:
- One is dextrorotatory (+)
- One is levorotatory (−)
- Their optical rotations cancel, so the mixture is optically inactive
Racemic Modification (Racemization)
- Racemization is the process of converting an optically active compound (pure enantiomer) into a racemic mixture.
-
How does it happen?
-
- Often occurs under the influence of:
- Heat
- Acids or bases
- Light
- Catalysts
-
- It involves the formation of a planar or achiral intermediate, allowing the creation of both enantiomers
-

Example:
- An optically active lactic acid (say, only the R-isomer) upon heating or in acidic solution can convert to a 50:50 mixture of R- and S-lactic acid.
Advertisements