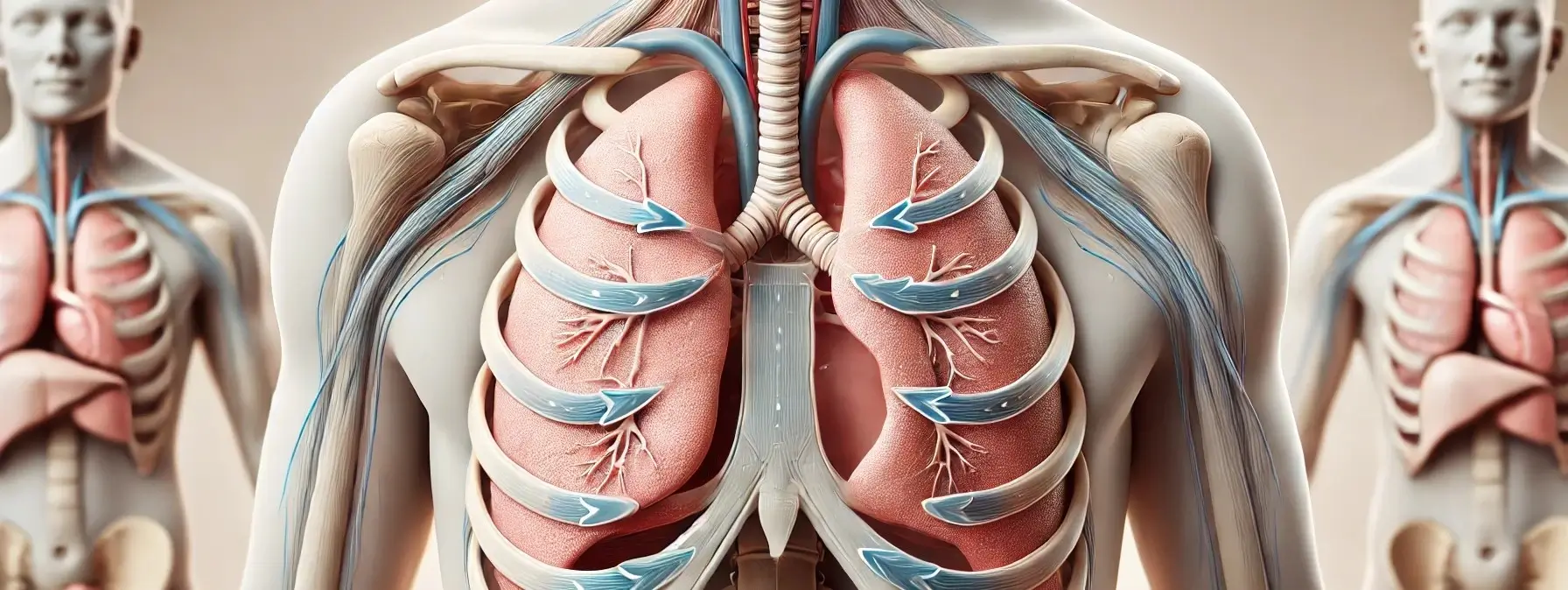
- Mechanism of respiration is the process by which the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment.
- Respiration of Mechanism can be divided into four main processes: ventilation, external respiration, internal respiration, and cellular respiration.
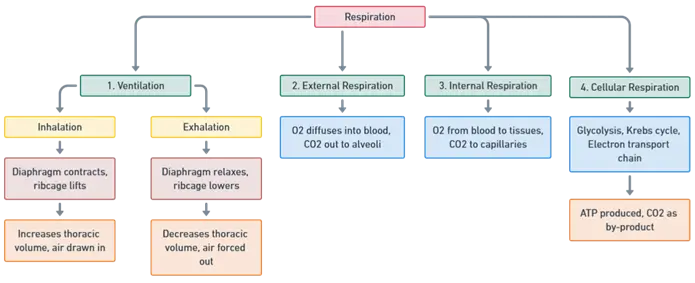
1. Ventilation (Breathing)
-
Inhalation:
- Mechanism: The diaphragm contracts and moves downward, while the external intercostal muscles lift the ribcage, expanding the thoracic cavity.
- Effect: This increases thoracic volume, creating negative pressure that pulls air into the lungs via the respiratory tract, reaching the alveoli.
-
Exhalation:
- Mechanism: The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax, decreasing the thoracic cavity’s volume.
- Effect: This creates positive pressure, pushing air out of the lungs.
2. External Respiration (Alveolar Gas Exchange)
- Location: Alveoli and pulmonary capillaries.
- Mechanism: Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood, binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Simultaneously: Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Advertisements
3. Internal Respiration (Tissue Gas Exchange)
- Location: Systemic capillaries and body tissues.
- Mechanism: Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs is pumped through systemic circulation.
- Oxygen diffuses from the blood into tissues, while carbon dioxide produced by cells diffuses into the blood.
- The carbon dioxide-rich blood returns to the lungs via the right side of the heart.
4. Cellular Respiration (Energy Production)
- Location: Mitochondria in cells.
- Mechanism: Cells use oxygen to produce ATP (energy) through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
- By-product: Carbon dioxide is produced and transported back to the lungs for elimination.