Teeth
- Teeth are hard, calcified structures in the mouth that play a crucial role in biting, tearing, and chewing food, as well as in speech and maintaining facial structure.
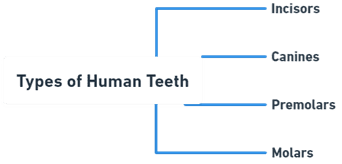
- Human teeth can be categorized into four main types, each serving a specific function:
Types of Teeth
Incisors:
- Location: Front of the mouth, four in the upper jaw and four in the lower jaw.
- Function: Flat and chisel-shaped, designed for biting and cutting food into smaller pieces.
Advertisements
Canines:
- Location: Next to the incisors, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower jaw.
- Function: Sharp and pointed, used for tearing and grasping food.
Premolars:
- Location: Next to the canines, four in each jaw.
- Function: Have a flat surface with two cusps, suitable for crushing and grinding food.
Molars:
- Location: At the back of the mouth, six in each jaw including the “wisdom teeth.”
- Function: Large and flat with a larger surface area for grinding and breaking down food into smaller particles.
Structure of a Tooth
Each tooth consists of several parts:
Crown:
- The visible part of the tooth above the gum line.
- Covered by enamel, the hardest substance in the human body, protecting the tooth from wear and decay.
Advertisements
Root:
- The part of the tooth embedded in the jawbone and not visible.
- Anchors the tooth to the bone, providing stability and support.
Enamel:
- The outermost layer of the tooth composed of a highly mineralized substance, primarily hydroxyapatite.
- Protects the tooth from wear, decay, and sensitivity to temperature and pressure.
Dentin:
- A calcified tissue that makes up most of the tooth structure beneath the enamel.
- Slightly softer than enamel but still provides strength and support to the tooth.
Advertisements
Pulp:
- The soft, innermost part of the tooth containing blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
- Provides nutrients to the tooth and responds to sensory stimuli such as temperature and pressure.
Cementum:
- A bone-like substance that covers the root of the tooth.
- Anchors the tooth to the surrounding periodontal ligament, helping to hold the tooth in place within the jawbone.
- Understanding the structure and types of teeth is essential for proper dental care and the effective use of dental products.