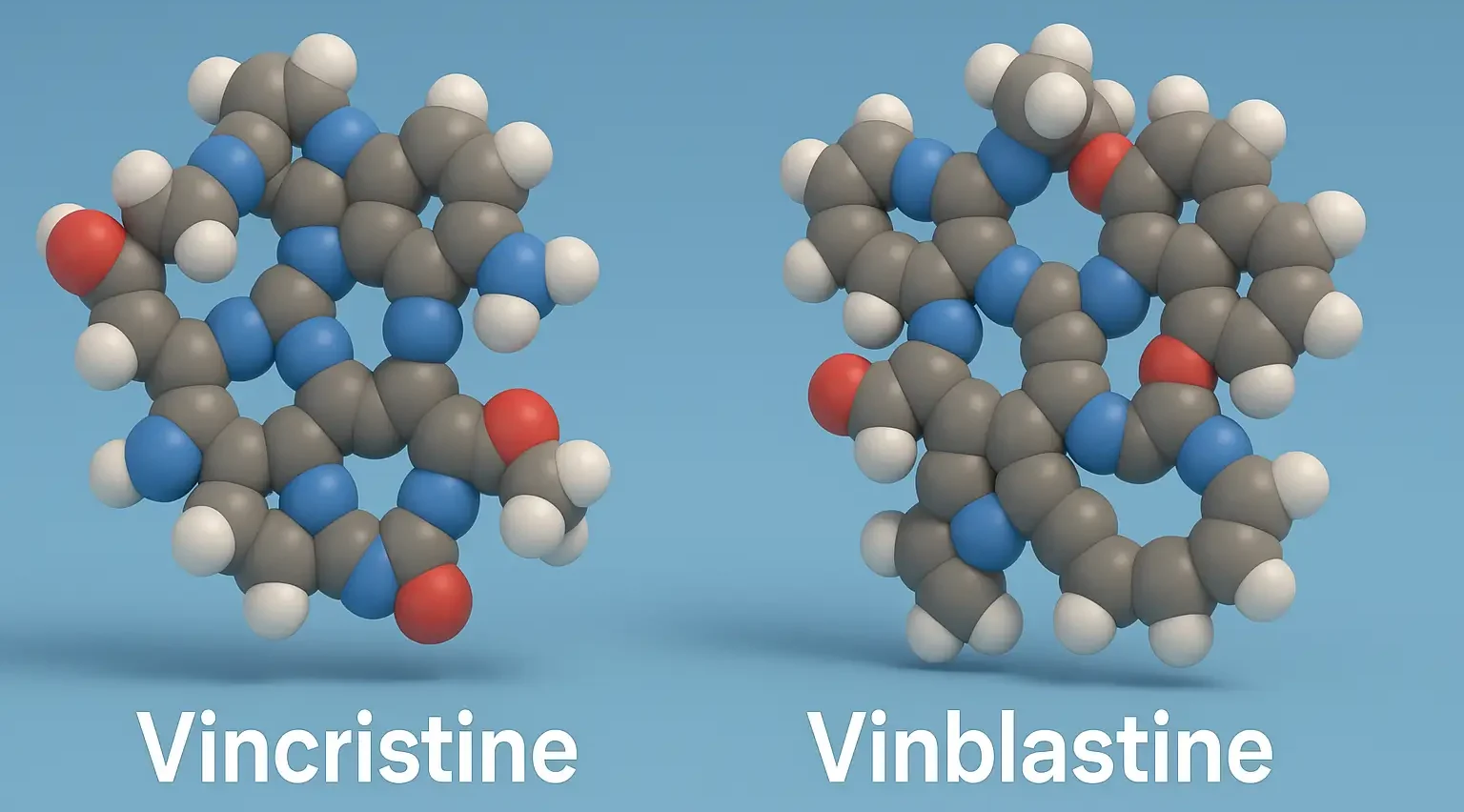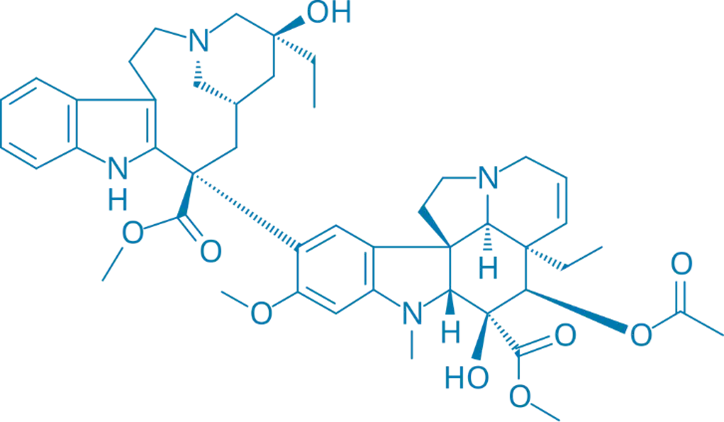
Industrial Production of Vincristine and Vinblastine
Source:
- Vincristine and vinblastine are alkaloids extracted from the Madagascar periwinkle plant, Catharanthus roseus (formerly Vinca rosea).

Extraction Process of Vincristine and Vinblastine:
- Cultivation: roseus is cultivated in controlled environments to maximize alkaloid content.
- Harvesting: Aerial parts (leaves and stems) are harvested, dried, and processed.
- Extraction: Solvent extraction using alcohols (e.g., ethanol) to solubilize vincristine and vinblastine.
- Isolation: Techniques such as liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography (e.g., reverse-phase HPLC), and crystallization separate the two alkaloids.
- Purification: Final purification steps ensure high-purity vincristine and vinblastine for pharmaceutical use.
Semi-Synthetic Production:
- Total Synthesis Challenges: The complex structures of vincristine and vinblastine make total chemical synthesis impractical for commercial production. Therefore, extraction from roseus remains the primary method.
- Biotechnological Approaches: Genetic engineering and plant cell culture techniques are being explored to enhance production yields.
Estimation
Analytical Techniques:
- HPLC: The standard method for quantifying vincristine’s and vinblastine’s in plant extracts and pharmaceutical formulations.
- LC-MS/MS: Provides high sensitivity and specificity for detailed molecular analysis.
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Utilized for routine monitoring based on characteristic absorbance.
- NMR Spectroscopy: Employed for structural confirmation and purity assessment.
Utilization
Pharmacological Applications:
- Anticancer Agents:
- Mechanism of Action: Both alkaloids disrupt microtubule formation, inhibiting mitosis and inducing apoptosis in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Other Uses:
- Research: Utilized in studies related to cell division, microtubule dynamics, and chemotherapy resistance mechanisms.
- Combination Therapies: Often used in multi-drug regimens to enhance therapeutic efficacy and mitigate resistance development.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!