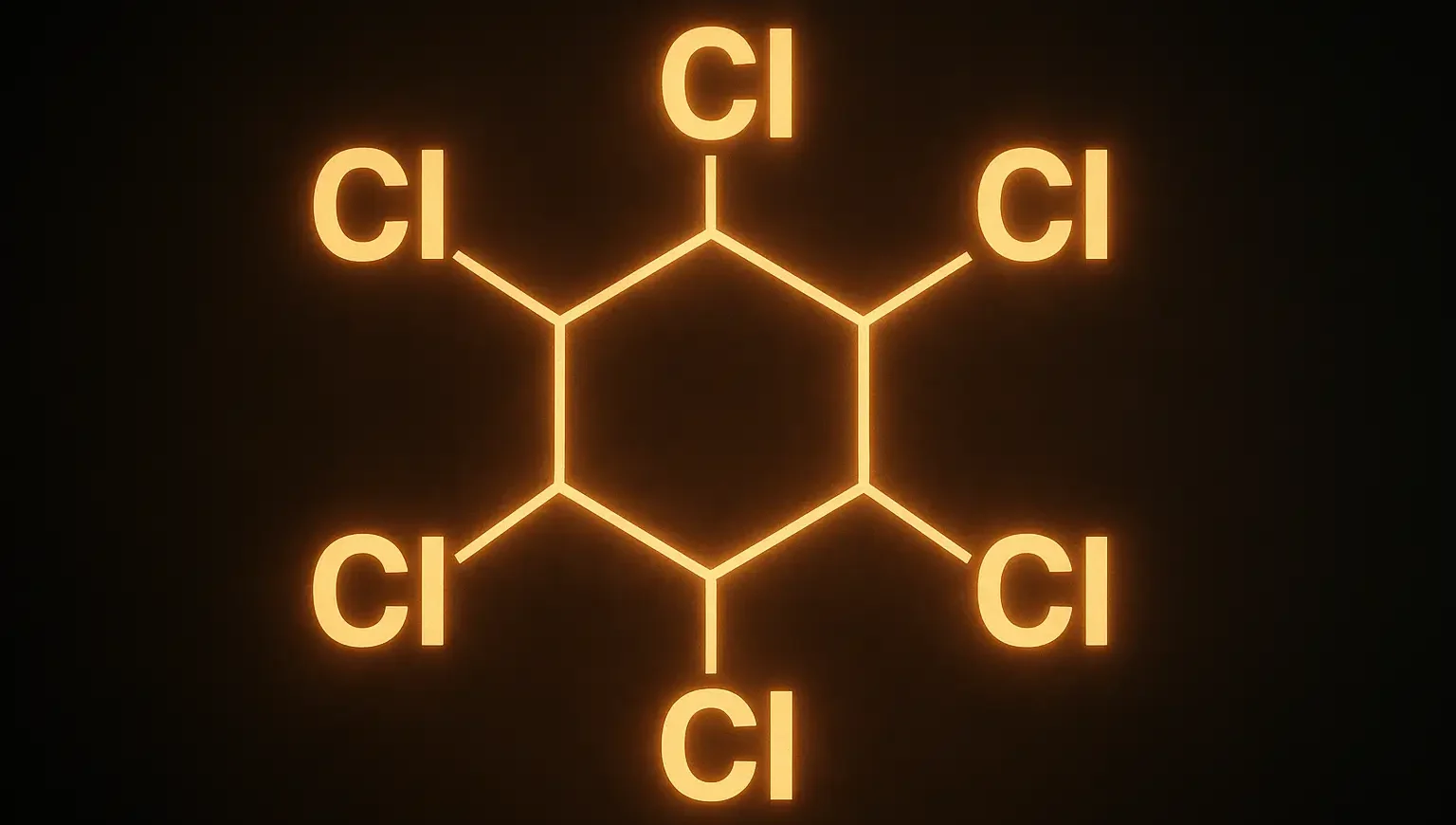
BHC (Benzene Hexachloride)
Structure of BHC (Benzene Hexachloride): Chemical Formula: C6H6Cl6 Description: BHC (Benzene Hexachloride), also known as hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), is an organochlorine compound. Its structure consists of a cyclohexane ring with six chlorine atoms attached. BHC exists in several isomers, with the gamma isomer (γ-HCH) being the most widely used and commercially significant. Uses: Used as an … Read more