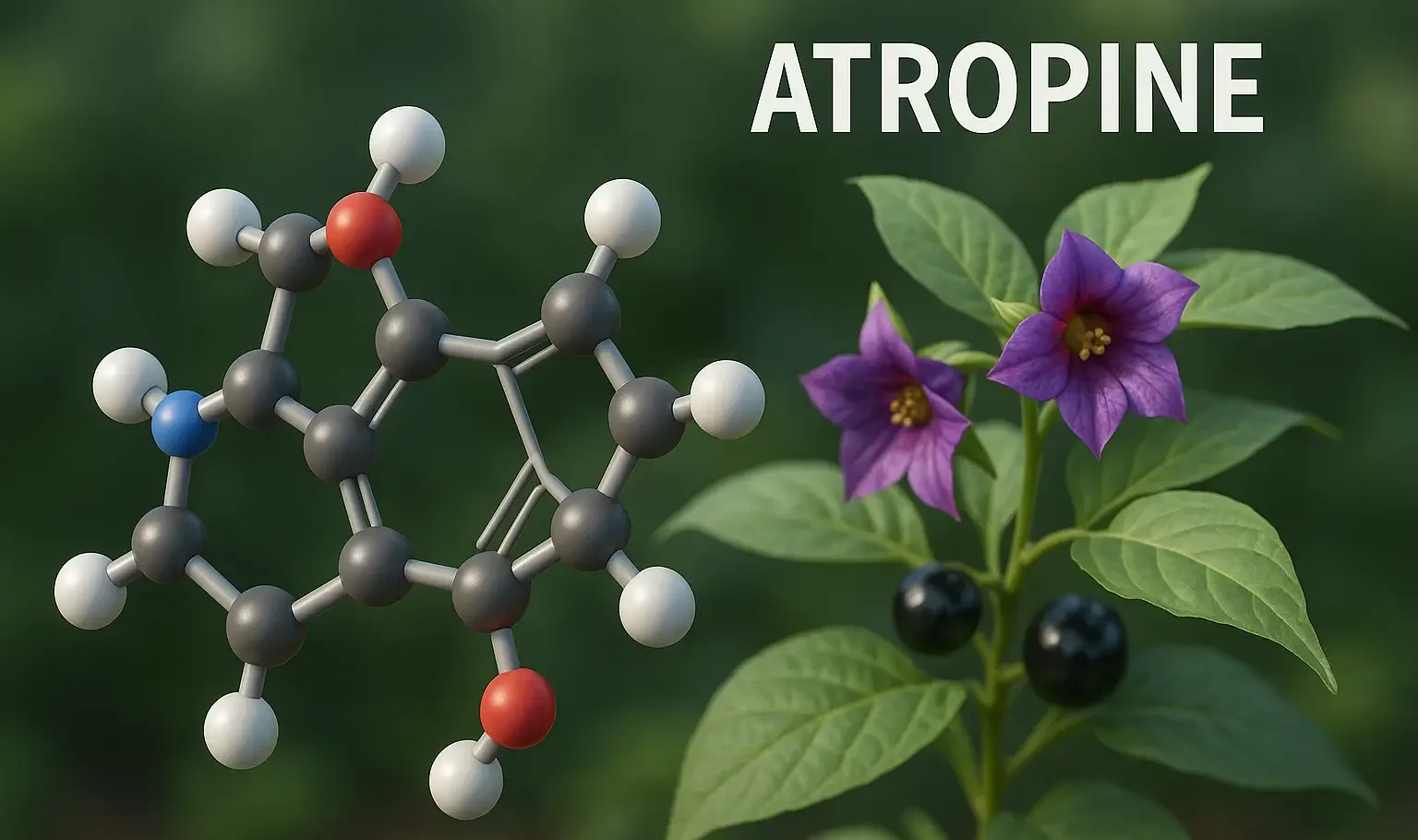
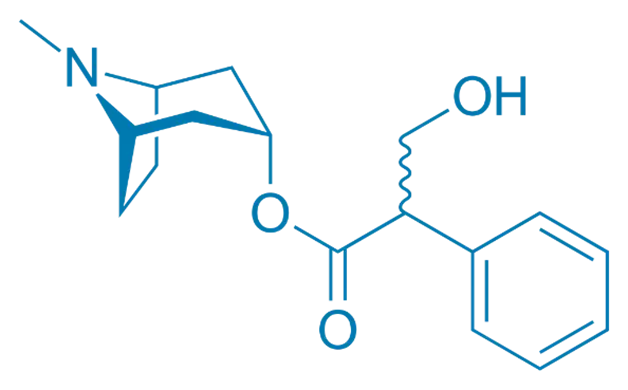
Source and Occurrence of Atropine

- Atropine is extracted from Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade), Datura stramonium (jimsonweed), and other Solanaceae family members.
- It is a tropane alkaloid with potent antimuscarinic properties.
Advertisements
Isolation
-
Extraction:
- Acid-Base Extraction:
- Acidic Extraction: Plant material is treated with an aqueous acid (e.g., HCl) to convert atropine into its water-soluble salt.
- Basification: The aqueous layer is basified with a strong base (e.g., NaOH) to free the atropine alkaloid, which is then extracted into an organic solvent like chloroform or ether.
- Acid-Base Extraction:
-
Purification:
Identification
-
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: White crystalline powder.
- Melting Point: Approximately 214-216°C.
- Solubility: Soluble in water as its hydrobromide or hydrochloride salts; soluble in organic solvents in free base form.
-
Spectroscopic Techniques:
- IR Spectroscopy: Detects functional groups such as hydroxyl groups and ester linkages.
- NMR Spectroscopy:
- ¹H NMR: Reveals signals corresponding to the tropane ring protons and methyl groups.
- ¹³C NMR: Confirms the carbon skeleton of atropine.
- Mass Spectrometry: Molecular ion peak at m/z 289 (free base).
-
Chromatographic Techniques:
- HPLC: Used for purity assessment and quantification.
- TLC: Standard method for monitoring extraction and purification stages.
Advertisements
Analysis
-
Quantitative Analysis:
- HPLC with UV Detection: Primary method for determining atropine levels in samples.
- Spectrophotometric Methods: Using specific reagents for colorimetric assays.
-
Quality Control:
- Ensuring the absence of other tropane alkaloids like scopolamine and hyoscyamine.
- Verifying structural integrity via spectral data.
Applications and Significance of Atropine
- Atropines are utilized as an antimuscarinic agent to treat bradycardia, as a mydriatic agent in ophthalmology, and as an antidote for organophosphate poisoning.
- Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it significant in both therapeutic and toxicological contexts.
Advertisements