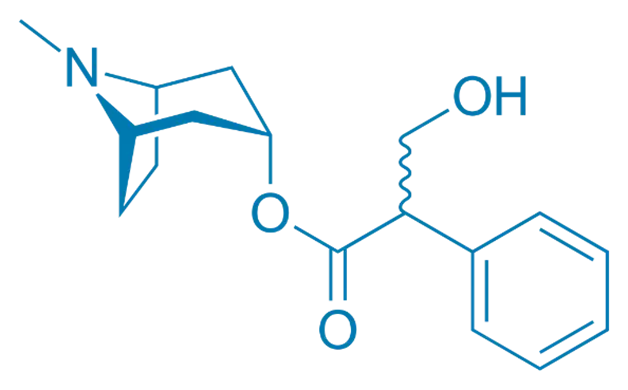
Industrial Production of Atropine
Source:
- Atropine is an alkaloid extracted from plants of the Solanaceae family, notably Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade), Datura stramonium, and Mandragora officinarum.

Advertisements
Extraction Process of Atropine:
- Cultivation: Plants are cultivated under controlled conditions to optimize alkaloid content.
- Harvesting: Aerial parts are harvested, dried, and processed.
- Extraction: Alkaline extraction using solvents like ethanol or methanol to solubilize atropine.
- Isolation: Liquid-liquid extraction and acid-base extraction methods separate atropine from other alkaloids.
- Purification: Techniques such as recrystallization, distillation, and chromatography achieve high purity atropines suitable for pharmaceutical use.
Alternative Production:
- Biotechnological Production: Plant cell cultures and microbial synthesis are areas of research, though extraction remains the primary method.
Advertisements
Estimation
Analytical Techniques:
- HPLC: Widely used for quantifying atropines in plant extracts and pharmaceutical formulations.
- GC-MS: Provides detailed molecular analysis and confirmation.
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Utilized for routine quantification based on absorbance properties.
- NMR Spectroscopy: Employed for structural confirmation and purity assessment.
Utilization
Pharmacological Applications:
- Antimuscarinic Agent: Used to treat bradycardia, reduce salivation during surgery, and as an antidote for organophosphate poisoning.
- Ophthalmology: Employed to dilate pupils during eye examinations.
- Pre-Anesthetic Medication: Reduces secretions and prevents bradycardia.
Advertisements
Other Uses:
- Toxicology: Atropine is studied for its role in poisonings and is a critical component in emergency medicine protocols.
- Research: Used in studies related to neurotransmission, particularly in cholinergic systems.