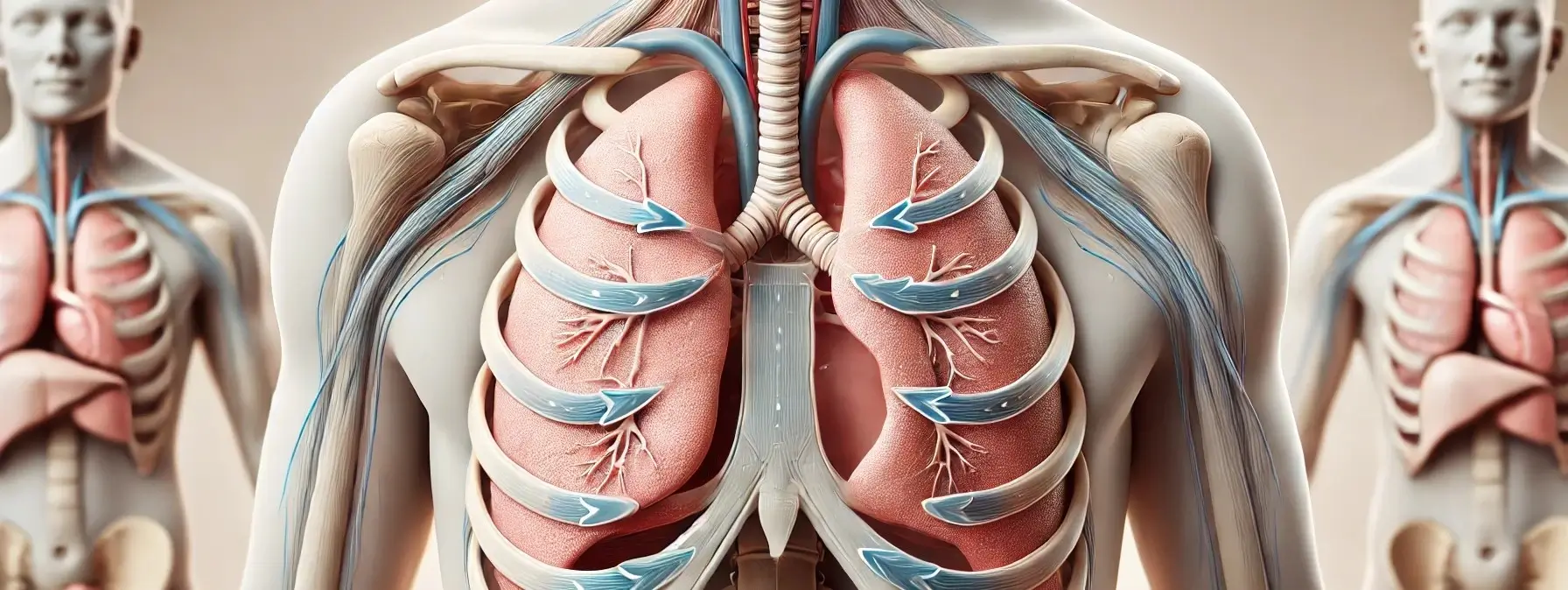
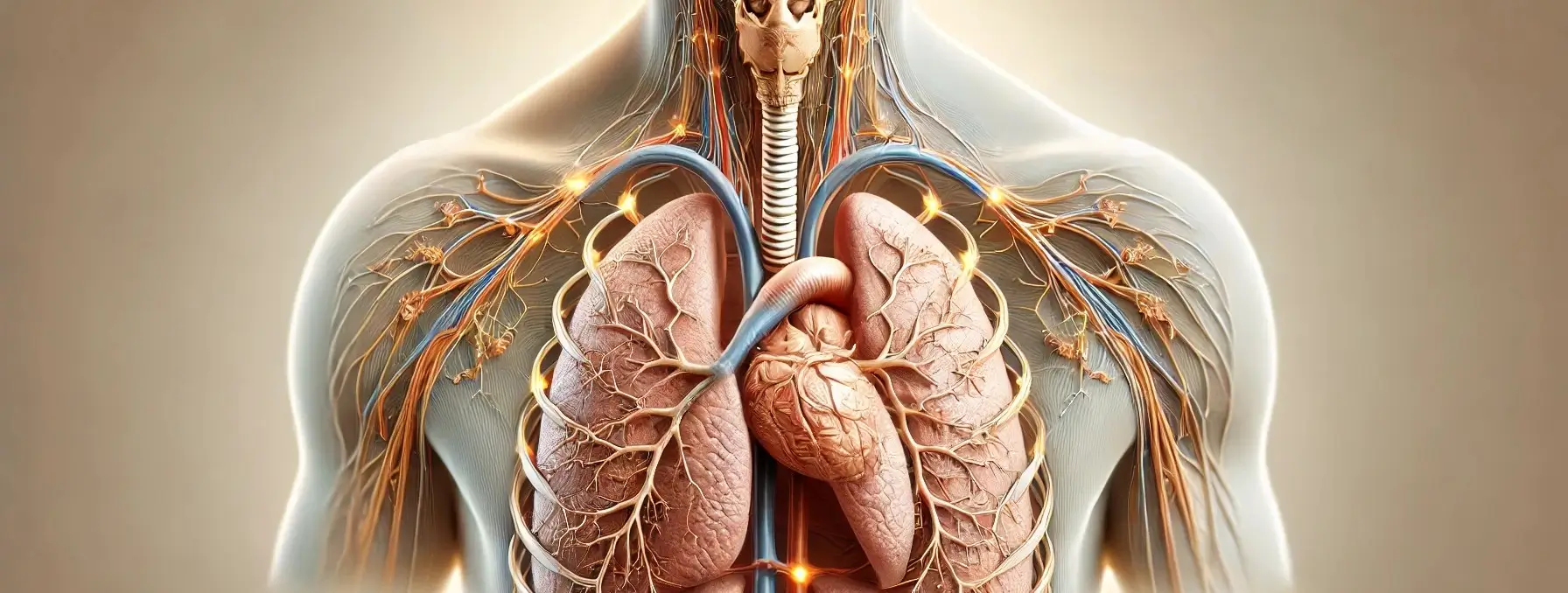
Mechanism of respiration
Mechanism of respiration is the process by which the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment. Respiration of Mechanism can be divided into four main processes: ventilation, external respiration, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. 1. Ventilation (Breathing) Inhalation: Mechanism: The diaphragm contracts and moves … Read more