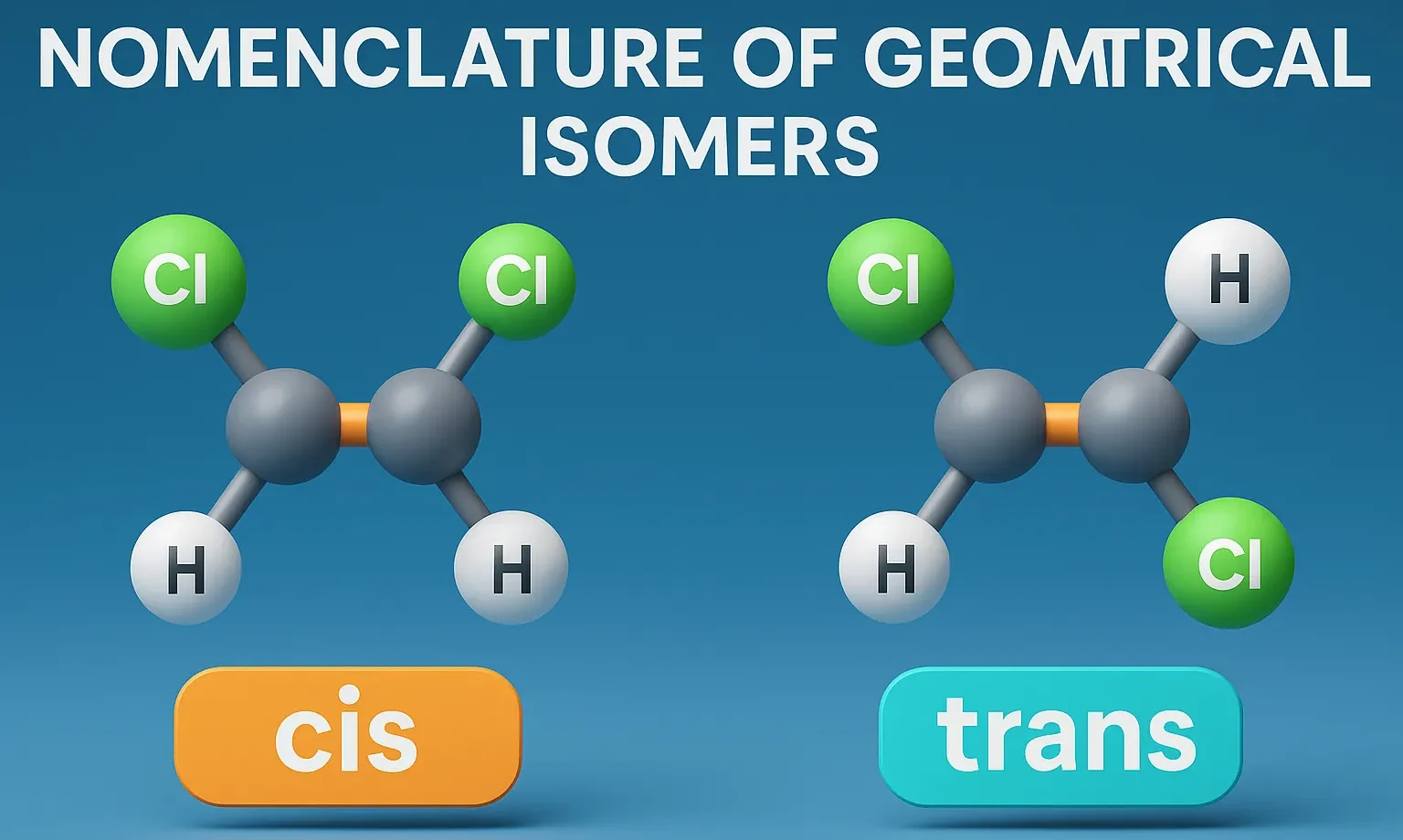
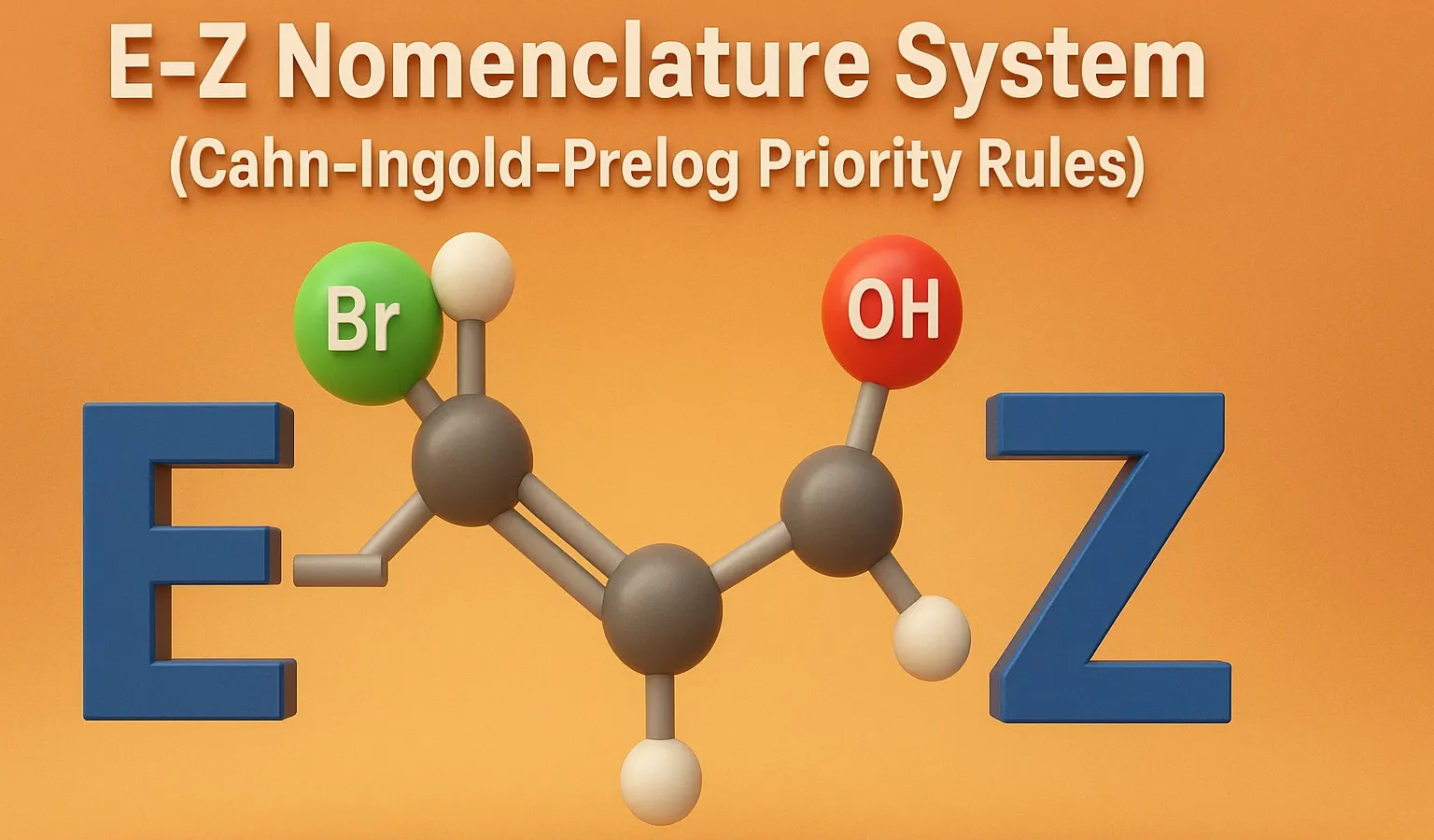
Thiophene
Thiophene is a five-membered aromatic heterocyclic compound with one sulfur atom, important in drugs, dyes, and conducting materials. Chemical Formula of Thiophene: C₄H₄S Physical Properties of Thiophene: Property Value Appearance Colorless to pale yellow liquid Odor Benzene-like Boiling Point 84 °C Melting Point -38 °C Solubility Soluble in organic solvents; poorly in water Density ~1.05 … Read more