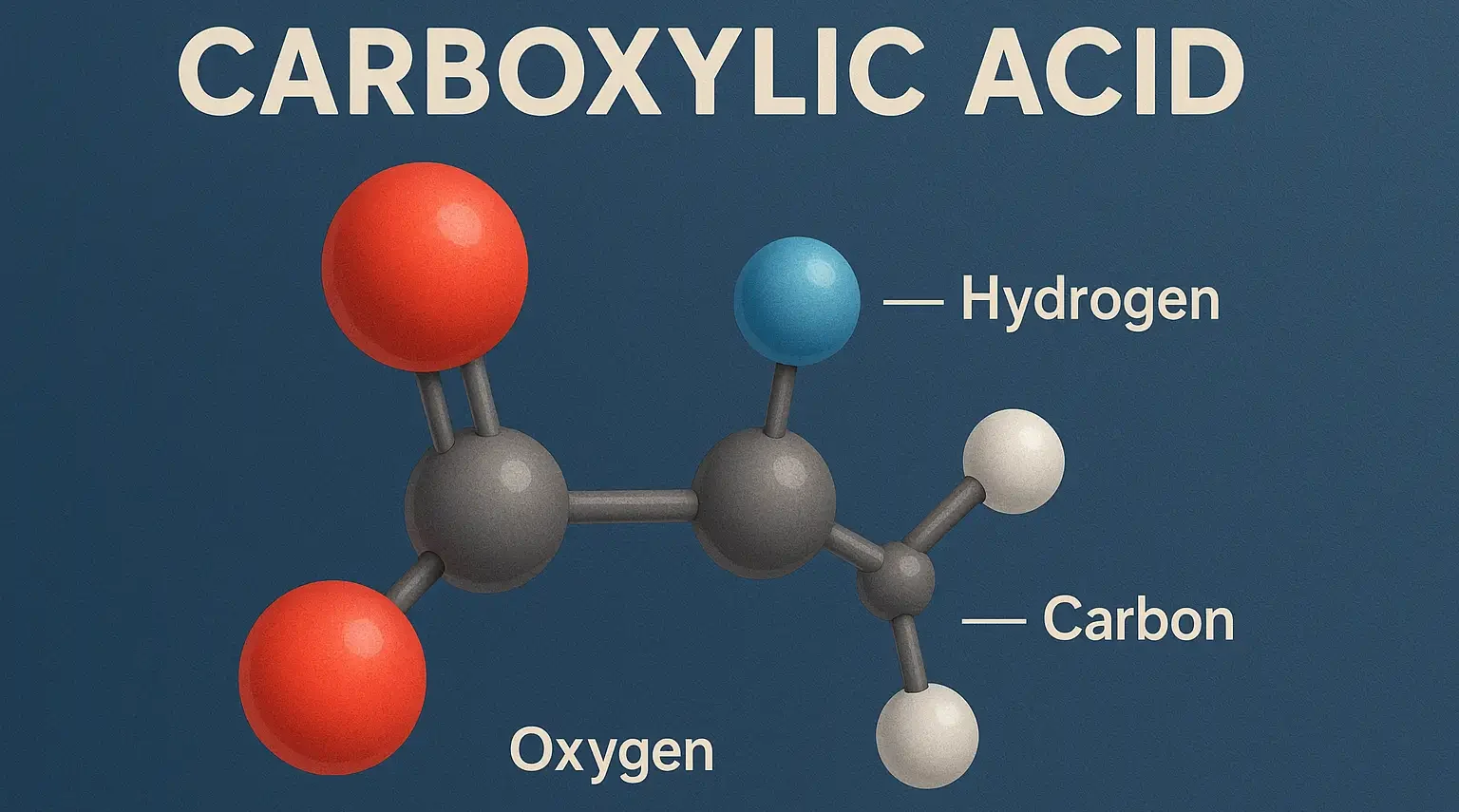
- Carboxylic acid is a fundamental class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH), which consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the same carbon atom.
- Carboxylic acid compounds exhibit weak acidic properties and versatile reactivity, making them crucial in many biological and industrial processes.
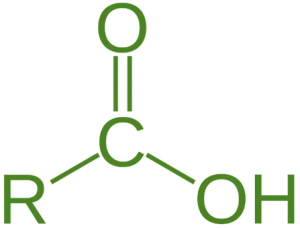
Classification of Carboxylic Acid
- Carboxylic acid can be categorized based on the nature of the carbon chain or ring attached to the carboxyl group:
-
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
- Saturated: No double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Examples include formic acid, acetic acid, and propionic acid.
- Unsaturated: One or more double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Examples include acrylic acid and sorbic acid.
-
Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
- Contain an aromatic ring attached to the carboxyl group. Examples are benzoic acid and salicylic acid.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Carboxylic acid
- Polarity: Carboxylic acids are polar due to the electronegative oxygen atoms, which enhances their solubility in water and other polar solvents, especially for lower-molecular-weight acids.
- Boiling and Melting Points: They have higher boiling and melting points compared to hydrocarbons or alcohols of similar size due to strong hydrogen bonding.
- Acidity: As weak acids, they can donate a hydrogen ion (H+). Their acidity is influenced by electron-withdrawing substituents and the resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion upon deprotonation.
- Reactivity: Carboxylic acids participate in several key reactions:
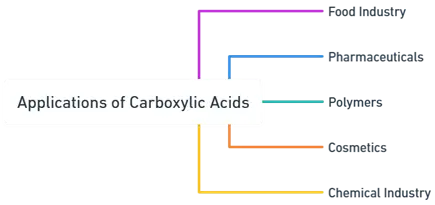
Applications of Carboxylic acid
-
Food Industry
- Preservatives: Benzoic acid inhibits microbial growth.
- Flavorings: Contribute to the flavor of food products.
- Acidity Regulators: Compounds like citric and acetic acids adjust acidity in beverages and vinegar.
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Polymers
- Polyesters and Polyamides: Adipic acid is used for nylon production, and terephthalic acid is used for PET polymers.
-
Cosmetics
-
Chemical Industry
- Serve as intermediates in the synthesis of esters, amides, and anhydrides, showcasing their versatility in chemical manufacturing processes.