Principle of Climbing Film Evaporator:
- Utilizes the principle of forming a thin film of liquid that climbs up the walls of a heated tube, enhancing evaporation due to increased surface area and reduced film thickness.
Construction of Climbing Film Evaporator:
- Vertical Tubes: Long, vertical tubes where the liquid forms a climbing film.
- Steam Jacket: Surrounds the tubes, providing the heat necessary for evaporation.
- Feed Inlet: Introduces the liquid at the bottom of the tubes.
- Vapor Outlet: For removing the evaporated vapor at the top.
- Concentrate Outlet: For removing the concentrated liquid.
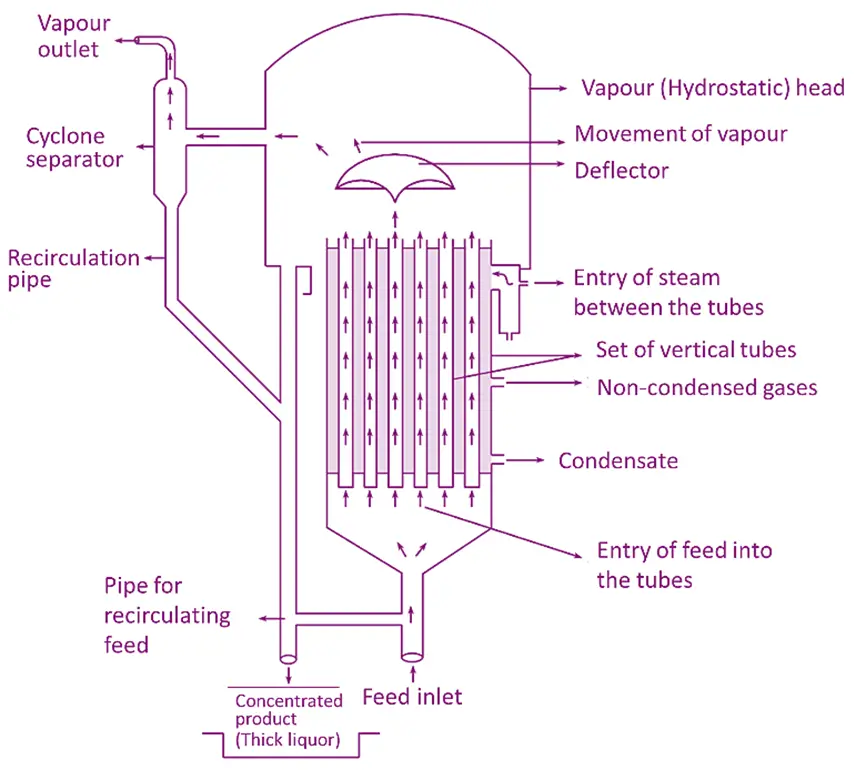
Working:
- The liquid is introduced at the bottom of the vertical tubes.
- As the liquid heats, vapor bubbles form, causing the liquid to rise and form a thin film on the tube walls.
- The film climbs up the tube due to the vapor’s upward force, evaporating along the way.
- Vapor is removed at the top, and the concentrated liquid exits through a separate outlet.
Advertisements
Uses:
- Concentration of heat-sensitive liquids in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
- Evaporation of solvents from solutions in the production of extracts and concentrates.
Merits:
- Efficient heat transfers due to the thin film and large surface area.
- Suitable for heat-sensitive materials due to short residence time.
- High evaporation rates.
Demerits:
- Complex design and operation.
- Requires precise control of feed rates and temperatures.
- High initial investment.