Source and Occurrence of Curcumin
- Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid found in Turmeric (Curcuma longa), a member of the ginger family.
- It is responsible for turmeric’s bright yellow color and has extensive applications in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Advertisements

Isolation
-
Extraction:
-
Purification:
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction: Partitioning between solvents of different polarities to isolate curcumin.
- Recrystallization: Curcumin is recrystallized from solvents like acetone or ethanol to achieve high purity.
-
Chromatography:
- Column Chromatography: Utilizing silica gel with solvent systems (e.g., hexane-ethyl acetate) to purify curcumin.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): For final purification steps.
Advertisements
Identification
-
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Bright yellow crystalline powder.
- Melting Point: Approximately 183°C.
- Solubility: Soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, acetone, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); sparingly soluble in water.
-
Spectroscopic Techniques:
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy: Strong absorbance around 420 nm due to conjugated double bonds.
- IR Spectroscopy: Identifies functional groups such as hydroxyl and methoxy groups.
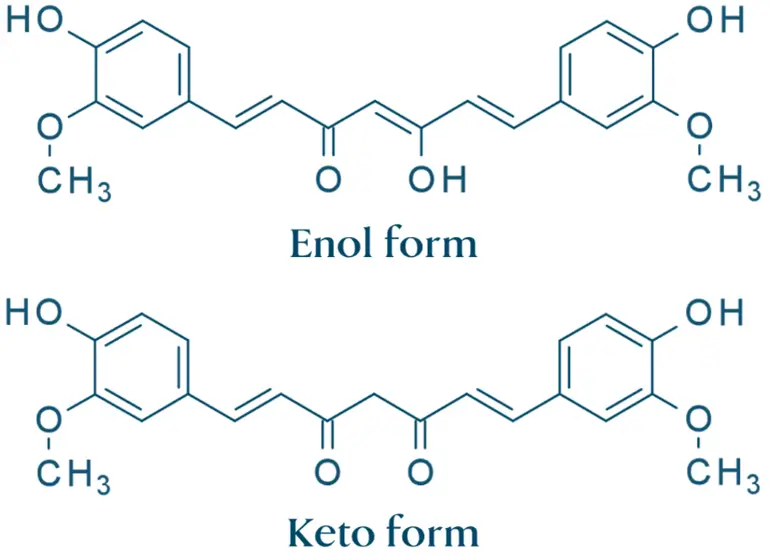
- NMR Spectroscopy:
- ¹H NMR: Reveals signals from aromatic protons, methoxy groups, and aliphatic chains.
- ¹³C NMR: Confirms the structure of curcumin.
- Mass Spectrometry: Molecular ion peak at m/z 368 (free base).
-
Chromatographic Techniques:
- HPLC: Essential for purity assessment and quantification.
- TLC: Used for monitoring extraction and purification stages.
Analysis
-
Quantitative Analysis:
- HPLC with UV Detection: Primary method for curcumins quantification in turmeric and formulations.
- Spectrophotometric Methods: Utilizing specific absorbance characteristics.
-
Quality Control:
- Ensuring high purity through HPLC profiles.
- Confirming structural integrity via spectral data.
Advertisements
Applications and Significance of Curcumin
- Curcumins are extensively used as a dietary supplement, food coloring agent, and in traditional medicine.
- It exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and neuroprotective activities, making it a subject of intense biomedical research.

