Industrial Production of Podophyllotoxin
Source:
- Podophyllotoxin is a lignan extracted primarily from the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum species, such as Podophyllum peltatum (mayapple) and Podophyllum emodi.
Advertisements
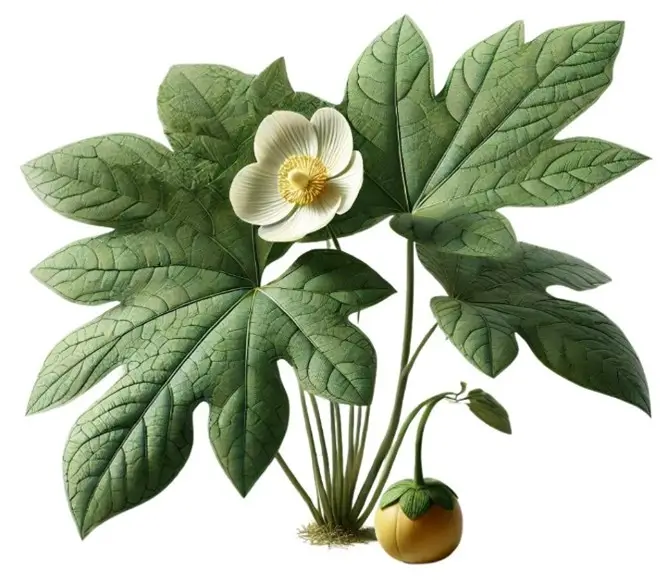

Extraction Process of Podophyllotoxin:
- Harvesting: Plant roots are harvested, cleaned, and dried.
- Extraction: Solvent extraction using alcohols like methanol or ethanol.
- Isolation: Liquid-liquid extraction and chromatographic techniques (e.g., silica gel chromatography) isolate podophyllotoxin.
- Purification: Recrystallization and additional chromatographic steps ensure high-purity podophyllotoxin suitable for pharmaceutical synthesis.
Advertisements
Alternative Production:
- Semi-Synthetic Derivatives: Podophyllotoxin serves as a precursor for various anticancer agents, such as etoposide and teniposide.
Estimation
Analytical Techniques:
- HPLC: The principal method for quantifying podophyllotoxins in plant extracts and pharmaceutical intermediates.
- GC-MS: Used for detailed analysis and confirmation of molecular structure.
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Utilized for routine monitoring based on specific absorbance.
- NMR Spectroscopy: Employed for structural verification and purity assessment.
Advertisements
Utilization
Pharmacological Applications:
- Anticancer Agents: Podophyllotoxins derivatives like etoposide and teniposide are used in chemotherapy for various cancers, including testicular cancer, lung cancer, and lymphomas.
- Topical Treatments: Podophyllotoxins itself is used in topical formulations to treat genital warts and other skin conditions due to its antiproliferative properties.
Other Uses:
- Research: Employed in studies related to cell division and mitosis due to its mechanism of action as a microtubule inhibitor.
- Agriculture: Investigated for potential uses as a natural pesticide, though not widely adopted.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

