Source and Occurrence of Reserpine
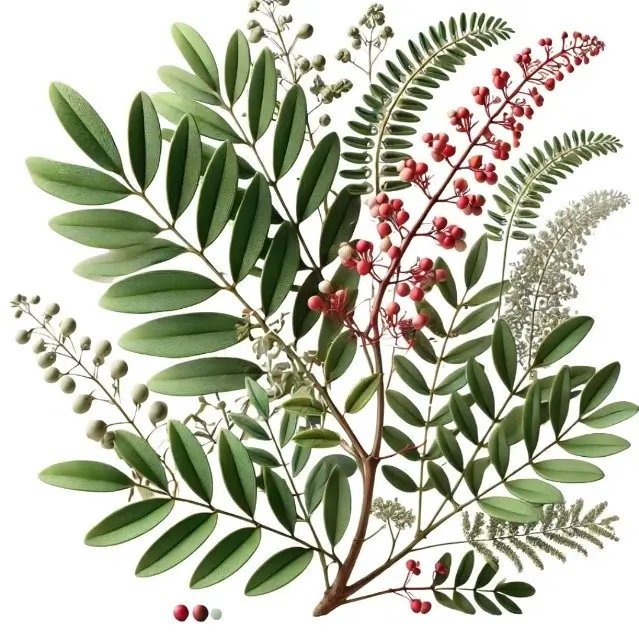

- Reserpine is extracted from the roots of Rauwolfia serpentina (Indian snakeroot) and Rauwolfia vomitoria.
- It is an indole alkaloid with antihypertensive and antipsychotic properties.
Advertisements
Isolation
-
Extraction:
-
Purification:
- Acid-Base Extraction:
- The extract is acidified to convert reserpine into its water-soluble salt.
- Basification liberates the free base, which is then extracted with an organic solvent like chloroform.
- Recrystallization: Reserpine is recrystallized from chloroform or ethanol to enhance purity.
- Acid-Base Extraction:
-
Chromatography:
- Column Chromatography: Using silica gel and appropriate eluent systems to purify reserpine.
Advertisements
Identification
-
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Yellowish crystalline powder.
- Melting Point: Approximately 190°C.
- Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, chloroform; insoluble in water.
-
Spectroscopic Techniques:
- IR Spectroscopy: Identifies functional groups such as indole ring and ester functionalities.
- NMR Spectroscopy:
- ¹H NMR: Reveals proton environments specific to the indole moiety and side chains.
- ¹³C NMR: Confirms the carbon framework of reserpine.
- Mass Spectrometry: Molecular ion peak at m/z 608 (free base).
-
Chromatographic Techniques:
- HPLC: For assessing purity and quantification.
- TLC: Monitoring extraction and purification stages.
Analysis
-
Quantitative Analysis:
- HPLC with UV Detection: Primary method for reserpines quantification.
- Spectrophotometric Methods: Using specific wavelengths corresponding to reserpine’s absorbance.
-
Quality Control:
- Ensuring the absence of other indole alkaloids like ajmalicine.
- Verification via spectral data.
Advertisements
Applications and Significance of Reserpine
- Reserpines are used as an antihypertensive agent by depleting catecholamines and serotonin from nerve terminals.
- It was also employed in psychiatric treatments for its antipsychotic effects, although its use has declined due to side effects.