Salicylic Acid
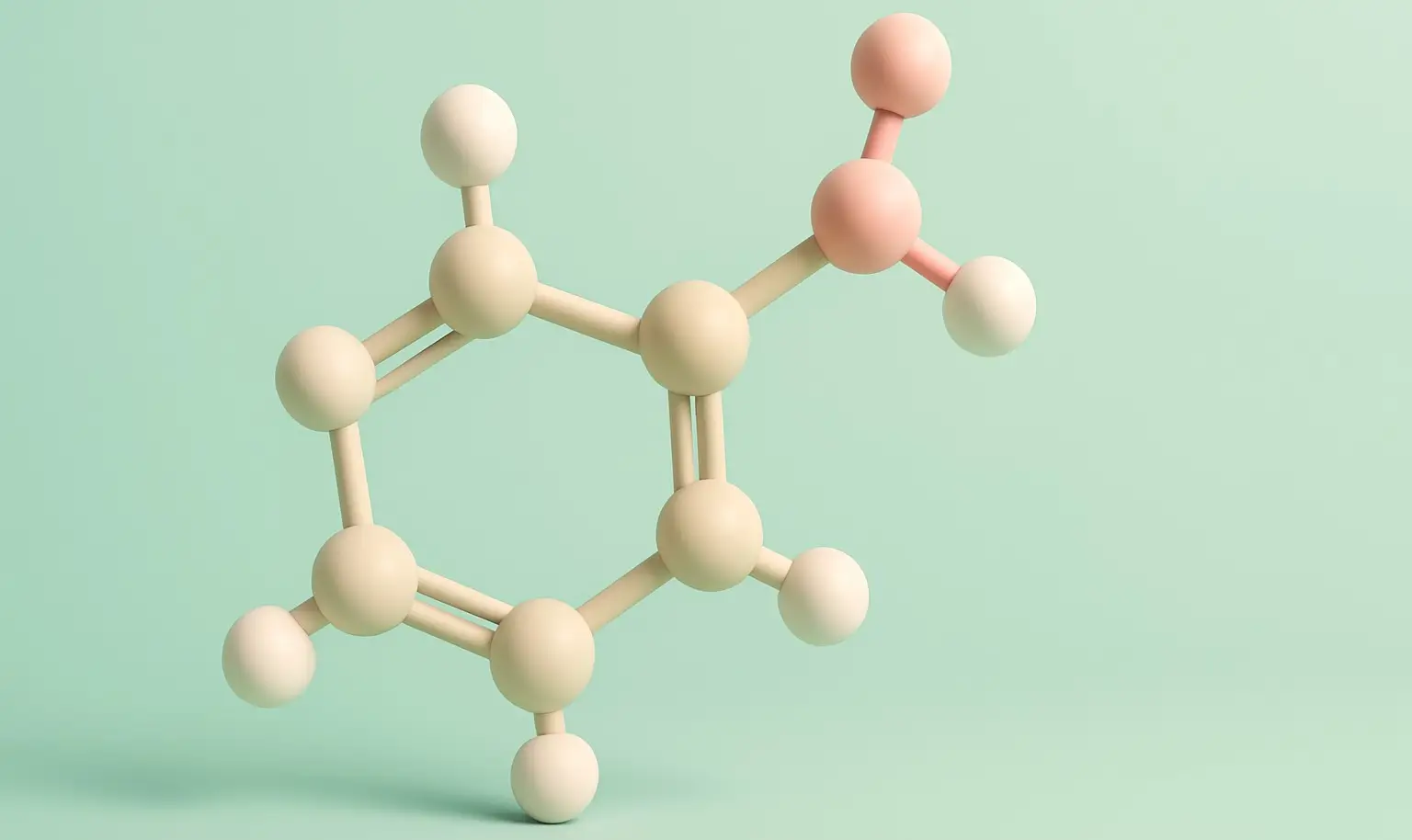
Salicylic Acid Definition Salicylic acid is a phenolic acid and a type of beta hydroxy acid that functions as a keratolytic, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial agent. It is commonly used to treat acne, warts, psoriasis, and other skin disorders due to its ability to exfoliate the skin and unclog pores. Structure: Chemical Formula: C₇H₆O₃ Molecular Structure: … Read more